Area circle calculator
The Area Circle Calculator is your go-to tool for quick, accurate, and hassle-free calculations of the area of a circle. Whether you're working on a school project, designing a layout, or simply curious about geometry, this calculator is designed to make your life easier.
Start using the Area Circle Calculator now and experience the ease of accurate, unit-friendly calculations for your everyday and professional needs!
Circle calculator
Most important parts of a circle
- Center: The point equidistant from all points on the circle's edge. It defines the circle's location and size.
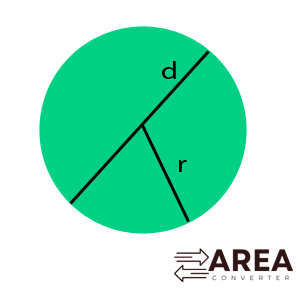
- Radius: The distance from the center to any point on the circumference. All radii of a circle are equal.
- Diameter: A line segment passing through the center that connects two points on the circumference. It is twice the radius.
- Circumference: The total distance around the circle. It is the circle’s perimeter, calculated as 2πr, where r is the radius.
- Chord: A line segment connecting two points on the circumference without necessarily passing through the center.
- Arc: A continuous portion of the circle’s circumference, measured in degrees or radians.
- Sector: A region of the circle enclosed by two radii and the arc between them, resembling a "slice" of the circle.
- Segment: A region of the circle enclosed by a chord and the arc above or below it.
- Tangent: A straight line that touches the circle at exactly one point. It is perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact.
- Secant: A line that intersects the circle at two points, extending beyond the circumference.
- Circumscribed circle: A circle that passes through all vertices of a polygon (e.g., a triangle) drawn inside it.
- Inscribed angle: An angle formed by two chords in the circle sharing an endpoint. Its vertex lies on the circumference.
How to calculate the area of a circle?
The area of a circle represents the total two-dimensional space enclosed within its boundary, known as the circumference. Mathematically, the calculation of a circle's area is derived from the relationship between the circle's radius (r) and the mathematical constant π (pi), an irrational number approximately equal to 3.14159. The formula for calculating the area is expressed as:
Here, A denotes the area, π accounts for the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, and r2 is the square of the radius. This formula is foundational in geometry and arises from the integration of the circle's radial dimensions, reflecting the cumulative infinitesimal areas of concentric rings forming the circle.
The radius is the distance from the circle’s center to any point on its edge, and squaring this value accounts for the two-dimensional nature of the area. The multiplication by π adjusts the proportional scaling between the radius squared and the circle’s true area.
This method is widely applicable in various scientific disciplines, such as physics for calculating cross-sectional areas in mechanics, biology for analyzing cell dimensions, and engineering for determining the space requirements of circular structures. The precision of this calculation relies on the accurate determination of the radius and the use of π to sufficient decimal places based on the context of the application.
How to calculate the circumference of a circle
To calculate the circumference of a circle, we use the fundamental geometric relationship between a circle’s radius and the constant π (pi). The formula is expressed as:
Alternatively, if the diameter d is known, the formula becomes C = π*d, since the diameter equals twice the radius.
To compute step by step: first, measure the circle’s radius or diameter accurately; next, substitute the value into the appropriate formula; then multiply by π (approximately 3.1416).
For example, if a circle has a radius of 7 cm, the circumference is C = 2 × π × 7 = 43.98 cm (rounded to two decimal places). This method provides a precise measure of the total distance around the circle, an essential calculation in engineering, architecture, and everyday geometry.
Why do we need the surface area of a circle calculators?
Calculators for the surface area of a circle are essential tools for several practical, scientific, and educational purposes. These calculators simplify and expedite the process of determining the area of a circle, especially in contexts where precision and efficiency are paramount. Below are the key reasons why these calculators are indispensable:
- Precision and accuracy
- Efficiency in real-time applications
- Unit conversion
- Educational value
- Wide range of applications
Math problems
-
Problem 1
Given: Radius \(r = 3\) cm.
Formula for area of a circle: \(A = \pi r^2\)
- Step 1: Write the formula: \(A = \pi r^2\).
- Step 2: Substitute the radius: \(A = \pi \times 3^2\).
- Step 3: Square the radius: \(3^2 = 9\).
- Step 4: Multiply by \(\pi \approx 3.14\): \(A = 3.14 \times 9 = 28.26\).
Answer: The area of the circle is 28.26 cm².
-
Problem 2
Given: Radius \(r = 5\) m.
Formula: \(A = \pi r^2\)
- Step 1: \(A = \pi r^2\).
- Step 2: Substitute: \(A = \pi \times 5^2\).
- Step 3: Square the radius: \(5^2 = 25\).
- Step 4: Multiply: \(A = 3.14 \times 25 = 78.5\).
Answer: The area of the circle is 78.5 m².
-
Problem 3
Given: Radius \(r = 12\) cm.
Formula: \(A = \pi r^2\)
- Step 1: \(A = \pi r^2\).
- Step 2: Substitute: \(A = \pi \times 12^2\).
- Step 3: Square the radius: \(12^2 = 144\).
- Step 4: Multiply: \(A = 3.14 \times 144\).
- Step 5: \(3.14 \times 144 = 452.16\).
Answer: The area of the circle is 452.16 cm².
-
Problem 4
Given: Radius \(r = 2.5\) m.
Formula: \(A = \pi r^2\)
- Step 1: \(A = \pi r^2\).
- Step 2: Substitute: \(A = \pi \times 2.5^2\).
- Step 3: Square the radius: \(2.5^2 = 6.25\).
- Step 4: Multiply by \(\pi \approx 3.14\): \(A = 3.14 \times 6.25\).
- Step 5: \(3.14 \times 6.25 = 19.625 \approx 19.63\) (rounded to 2 decimals).
Answer: The area of the circle is 19.63 m².
FAQ – Circle Area Calculator
What is the formula to calculate the area of a circle?
The area of a circle is given by A = πr², where r is the radius and π (pi) ≈ 3.1416. This formula expresses the space enclosed within the circle’s boundary.
How can I find the radius if the area of a circle is known?
To find the radius, rearrange the formula to r = √(A / π). Divide the area by π, then take the square root to determine the circle’s radius.
What are common uses of the circle area formula?
The circle area formula is applied in geometry, engineering, and design to calculate surface coverage, material usage, and spatial dimensions of circular objects.
